Red tide is a captivating natural phenomenon that occurs when the concentration of algae in the water rises dramatically. Not only does it mesmerize with its vibrant red hue, but it also poses risks to marine life, humans, and the environment. Let’s dive deeper into the causes and types of red tide, shedding light on this fascinating yet concerning phenomenon.
What Causes Red Tide?
Red tide is a complex interplay of environmental conditions and human activities. The most common cause stems from an overabundance of certain species of algae, which can occur naturally or due to human interference. These algae thrive in warm, nutrient-rich waters, explaining why red tide outbreaks are prevalent in areas with agricultural runoff, sewage discharge, or other human activities that raise nutrient levels in the water.
Types of Red Tide

Several types of red tide exist, each with its own characteristics and effects. The most prevalent is the dinoflagellate red tide, caused by a type of algae called Karenia brevis. This algae species produces a toxin that can cause respiratory problems in humans and be fatal to marine life.
Another type of red tide arises from diatoms, minute algae that produce a biotoxin known as domoic acid. This specific red tide variant can lead to severe neurological damage in humans and animals that consume contaminated seafood. Blue-green algae and brown algae can also trigger red tide, producing diverse toxins and influencing the environment and human health in different ways.
Red tide outbreaks can emerge in both saltwater and freshwater environments, lasting anywhere from a few weeks to several months. The severity of the outbreak depends on factors such as the algae’s type, toxin concentration, and the environmental conditions within the affected area.
Impact of Red Tide

Red tide carries significant implications for marine life, human health, and the economy. The toxins generated by the algae can induce various health problems in both humans and animals. Moreover, the environmental damage caused by red tide can leave long-lasting effects on the delicate ecosystem.
Effects on Marine Life
Red tide proves deadly for marine life, especially fish, shellfish, sea turtles, and marine mammals. The toxins released by the algae can lead to neurological damage, respiratory issues, and paralysis in some species. Additionally, red tide outbreaks can deplete oxygen levels in the water, creating “dead zones” where marine life cannot survive.
Effects on Human Health
The toxins produced by red tide can also have adverse effects on human health, particularly for those who consume contaminated seafood or inhale the toxins present in the air. Red tide poisoning symptoms may include respiratory problems, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, confusion, and even fatalities in severe cases.
Economic Impact
Coastal communities relying on fishing, tourism, and other marine-related industries suffer significant economic setbacks due to red tide outbreaks. The closure of fishing grounds and beaches to safeguard human health and the environment results in substantial financial losses for local businesses. These closures can have enduring effects on the local economy.
Monitoring and Management of Red Tide
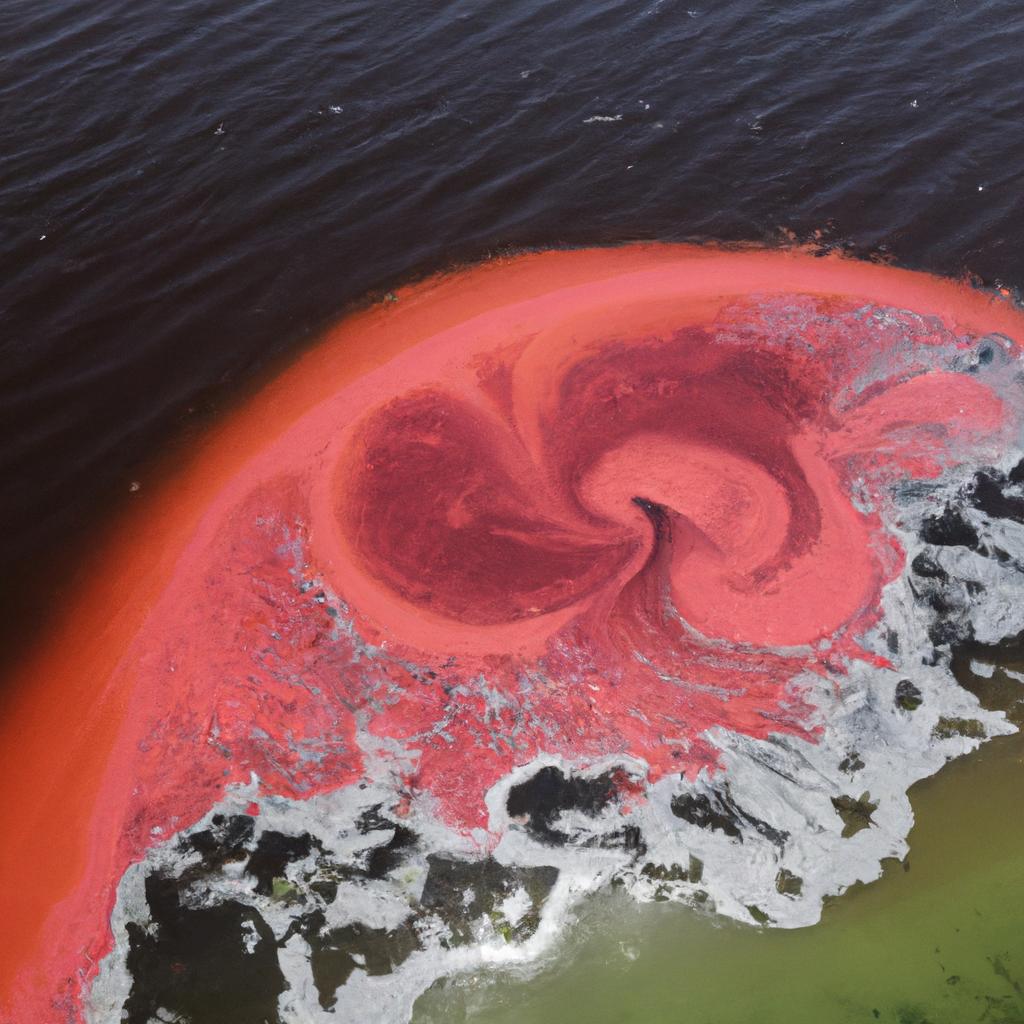

Efficient monitoring and management of red tide outbreaks are essential for minimizing their impact on the environment, human health, and the economy. Several methods aid in monitoring red tide, such as satellite imagery, water sampling, and the use of underwater sensors. These techniques enable early detection of red tide outbreaks, facilitating prompt action.
To manage red tide outbreaks, strategies like employing biodegradable surfactants to disperse the algae, introducing natural predators that feed on the algae, and implementing filtration systems to remove toxins from the water prove valuable. In certain cases, it becomes necessary to close fishing grounds and beaches to safeguard human health and the environment.
Continual research aims to develop novel methods for monitoring and managing red tide outbreaks. Genetic engineering, for example, holds potential for creating algae strains resistant to the environmental conditions that trigger red tide. Although these methods are still in the early stages of development, they offer promises of more effective and sustainable red tide management in the future.
Prevention of Red Tide
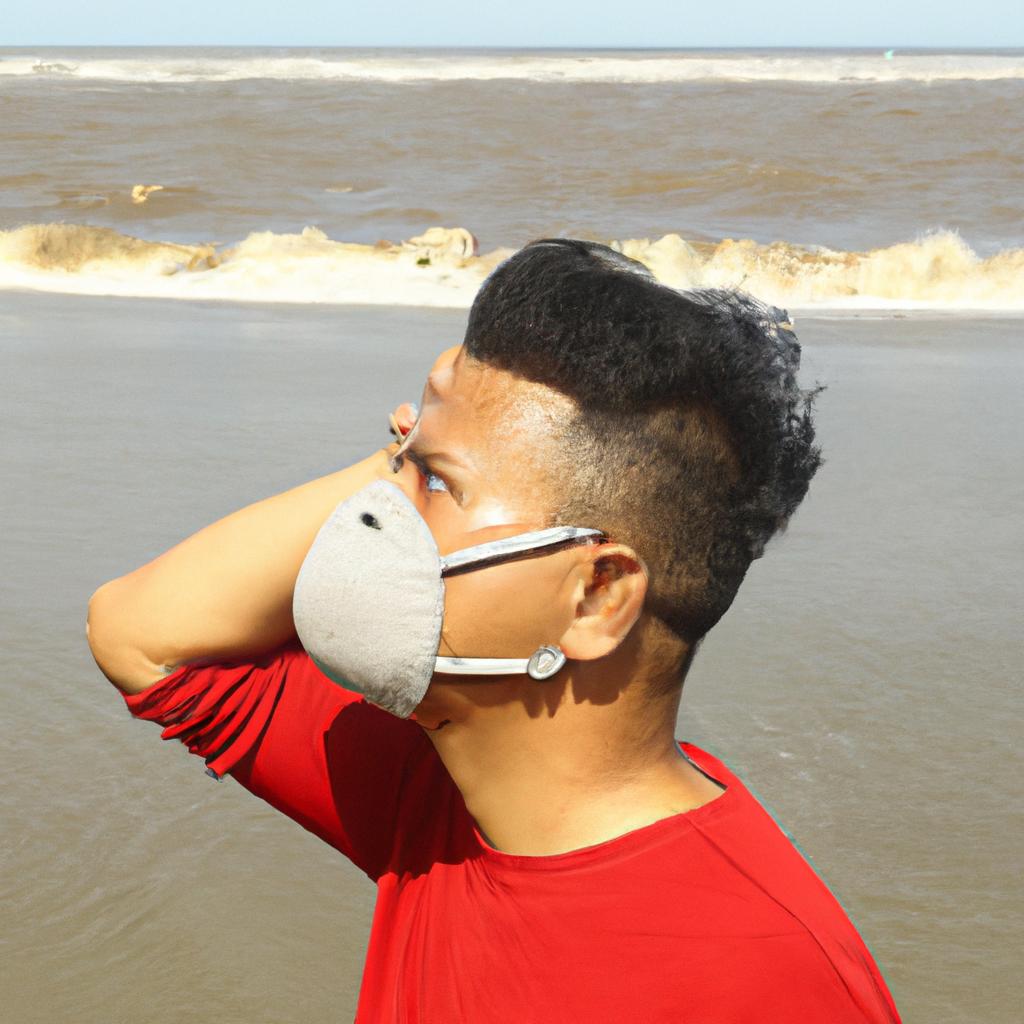

Preventing red tide outbreaks requires a multifaceted approach that combines preventative measures and research on red tide prevention. Here are a few measures that can help prevent red tide outbreaks:
1. Reducing Nutrient Levels in the Water
Since red tide outbreaks often stem from an excess of nutrients in the water, reducing nutrient levels proves effective in preventing these outbreaks. This can be achieved by curbing agricultural runoff, sewage discharge, and other human activities that elevate nutrient levels in the water.
2. Developing Alternative Aquaculture Practices
Traditional aquaculture practices can contribute to red tide outbreaks by increasing nutrient levels in the water. Developing alternative practices, such as closed-loop systems and integrated multi-trophic aquaculture, can mitigate the impact of aquaculture on the environment and prevent red tide outbreaks.
3. Monitoring and Early Detection
Monitoring and early detection of red tide outbreaks play a vital role in preventing the spread of algae and reducing the impact on marine life and human health. Developing effective monitoring systems and early detection methods remains critical in preventing red tide outbreaks.
Conclusion
Red tide outbreaks present significant environmental and public health concerns, carrying grave consequences for marine life, human health, and the economy. Although the causes of red tide are intricate, preventative measures and ongoing research on red tide prevention provide hope for managing and preventing these harmful algae blooms.
In conclusion, reducing nutrient levels in the water, developing alternative aquaculture practices, and implementing monitoring and early detection measures all play essential roles in preventing red tide outbreaks. With continued research and development, we can enhance our understanding of red tide and devise effective strategies to prevent and manage these harmful algae blooms. At TooLacks, we remain committed to delivering the latest news and information on red tide and other environmental issues that impact our world today.



