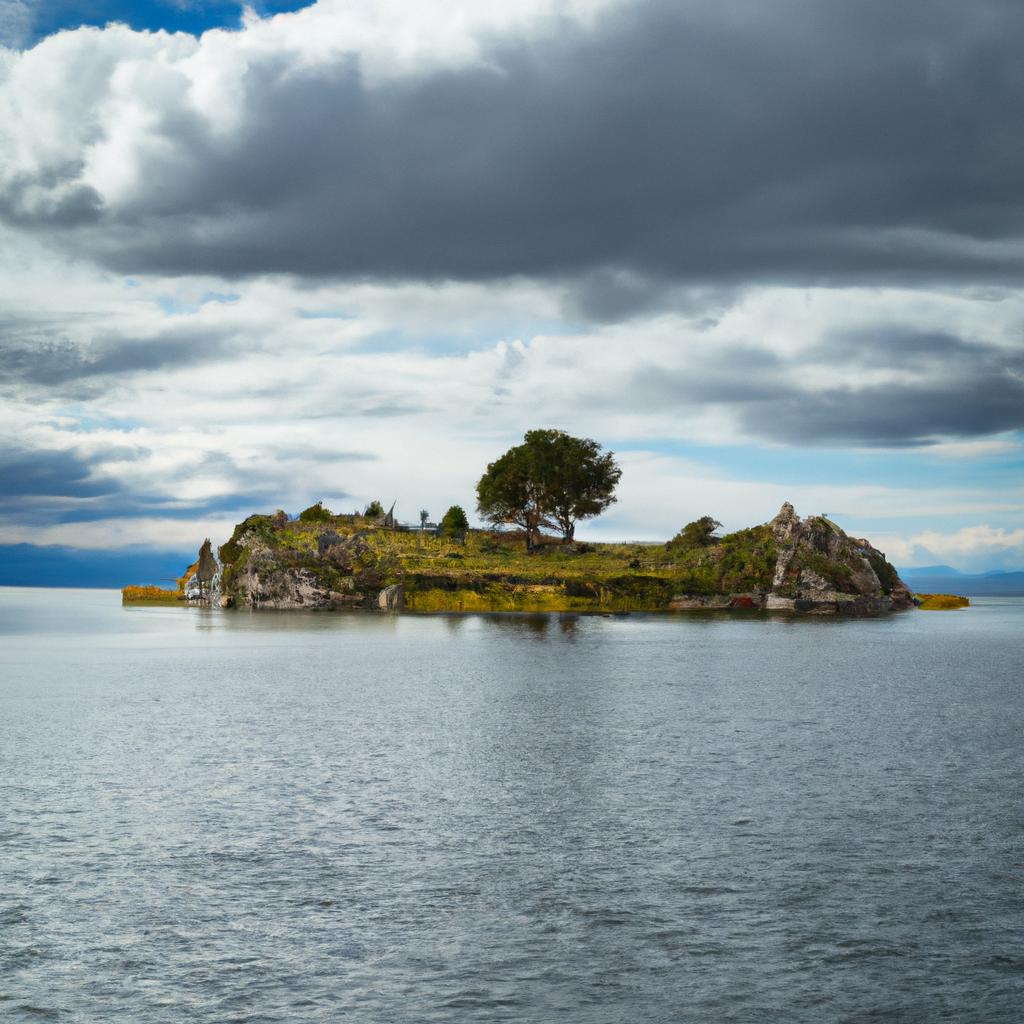
Are you ready for a remarkable travel experience? Look no further than Lake Titicaca and its breathtaking islands. Nestled in the Andes Mountains of South America, Lake Titicaca stands as the highest navigable lake globally, positioned at an altitude of over 12,500 feet. Not only does this lake possess awe-inspiring beauty, but it also holds deep cultural significance.
The History of Lake Titicaca Islands
The Origins and Formation of the Lake
Lake Titicaca serves as a remnant of a colossal prehistoric lake that once covered much of the Andean region. Over millions of years, this lake gradually formed through tectonic activity and glacial melting. With an estimated age of around 3 million years, Lake Titicaca is one of the oldest lakes on our planet.
Pre-Columbian Civilizations that Inhabited the Islands
Inhabited by indigenous peoples for thousands of years, the islands surrounding Lake Titicaca hold a fascinating history. The Tiwanaku civilization thrived in the area from around 400 AD to 1000 AD, leaving their mark on the region. The Inca Empire followed, conquering the land in the 15th century.
The Incas regarded Lake Titicaca as sacred, believing that their deity, Viracocha, emerged from its depths to create the world. They constructed several temples and shrines on the islands, including the remarkable Temple of the Sun on the Island of the Sun.
Spanish Conquest and Its Impact on the Islands
The Spanish arrived in South America in the 16th century and conquered the Inca Empire. This conquest had a profound influence on the islands and their inhabitants. Many temples and shrines were destroyed, and the indigenous population was coerced into converting to Christianity.
Despite the destruction and forced conversion, the indigenous communities valiantly preserved their traditions and customs. Today, these islands are home to numerous indigenous groups, such as the Uros, who reside on floating islands crafted from reeds.
Geographical Features of Lake Titicaca Islands
The islands of Lake Titicaca boast unique geological formations unparalleled anywhere else on Earth. Surrounded by towering peaks in the Andes Mountains, the lake provides a spectacular backdrop for these islands. Let’s delve into the geographical wonders of the Lake Titicaca islands:
Overview of the Islands and their Locations
Lake Titicaca encompasses over 70 islands, each with its own captivating history and culture. On the Bolivian side, you’ll find the largest islands, Isla del Sol and Isla de la Luna. On the Peruvian side, you’ll encounter the renowned Uros Islands, constructed entirely with reeds. Exploring these floating islands is an absolute must for any visitor.
Unique Geological and Environmental Characteristics
Most notably, Lake Titicaca’s high altitude sets it apart. Sitting over 12,500 feet above sea level, it reigns as the world’s highest navigable lake. The lake’s crystal-clear waters, fed by numerous rivers and streams, add to its allure.
The surrounding landscape is dominated by the Andes Mountains, housing diverse wildlife, including the majestic Andean condor, one of the largest flying birds on Earth.
Flora and Fauna Found in the Islands
The islands of Lake Titicaca shelter a variety of flora and fauna, including rare bird species like the Titicaca grebe and the Andean flamingo. The lake is also a refuge for numerous fish species, including the exclusive Titicaca orestias.
The lake’s unique environmental conditions have fostered the evolution of countless endemic plant and animal species, underscoring its ecological significance.
Cultural Significance of Lake Titicaca Islands
Lake Titicaca and its islands occupy a significant place in Incan mythology and religion. The Incas believed that the lake served as the birthplace of their civilization, where the god Viracocha emerged and brought about the creation of the sun, moon, stars, and humanity.
To this day, the islands remain homes to indigenous communities diligently preserving their traditional customs and practices. Among these communities are the Uros, renowned for living on the astonishing floating reed islands. The larger islands are inhabited by the Quechua and Aymara peoples.
Visitors to these islands can bear witness to traditional ceremonies and festivals, including the vibrant Virgen de la Candelaria festival held in February. This celebration pays homage to the region’s rich cultural heritage, featuring captivating music, dance, and colorful parades.
However, the preservation of these islands’ cultural heritage faces threats due to the impact of colonialism and modernization. Discrimination and external influences have disrupted the traditional way of life of indigenous communities.
Nonetheless, efforts are underway to safeguard the islands’ cultural heritage. The Peruvian government has designated Lake Titicaca as a protected area, and organizations like the Titicaca Ecological Reserve work tirelessly to promote sustainable tourism and protect both the environment and local communities.
Tourism in Lake Titicaca Islands
The splendid beauty and cultural significance of Lake Titicaca and its islands have made it a popular destination for travelers worldwide. Let’s explore some of the most sought-after tourist attractions and activities on these islands:
Popular Tourist Attractions and Activities in the Islands
-
Uros Islands: These mesmerizing floating islands, crafted from reeds, have been inhabited by indigenous communities for centuries. Embark on a tour to learn about the unique way of life of the Uros people.
-
Taquile Island: As the largest island, Taquile is renowned for its textile production. Witness the intricacies of the weaving process and discover high-quality handmade textiles available for purchase.
-
Amantani Island: Immerse yourself in the traditional way of life by staying overnight with local families. Enjoy the island’s stunning views and hiking trails.
-
Isla del Sol: Located on the Bolivian side, Isla del Sol is believed to be the birthplace of the Inca civilization. Discover ancient ruins and savor breathtaking views of the lake.
Sustainable Tourism Practices and Their Impact on the Islands
While tourism has brought economic benefits to the communities around Lake Titicaca, it has also posed challenges. Sustainable tourism practices aim to minimize the negative impact on both the environment and local communities. Some of these practices include:
-
Community-based tourism: Experience the local culture and customs firsthand by staying with local families.
-
Eco-tourism: Preserve the environment and minimize the impact of tourism on the natural habitats surrounding Lake Titicaca.
-
Responsible tourism: Encourage visitors to respect local culture and customs while minimizing their impact on the environment.
Challenges and Opportunities for Tourism Development in the Region
While tourism has generated economic benefits, it has also presented challenges. The delicate ecosystem around Lake Titicaca is at risk due to pollution and overuse. However, tourism also offers opportunities for sustainable development. By implementing sustainable practices, the economic benefits of tourism can be maximized while minimizing the negative impact on the environment and local communities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Lake Titicaca and its islands stand as an unparalleled destination that seamlessly blends breathtaking natural beauty, captivating cultural heritage, and extraordinary wildlife. This remote gem, with its high altitude and untouched splendor, serves as a testament to the rarity of our world.
Visiting the islands of Lake Titicaca offers an opportunity to immerse yourself in a way of life that has endured the test of time. The warm embrace of the local communities invites you to explore their customs and traditions. The floating islands made of reeds showcase the remarkable engineering prowess of the local people.
Moreover, Lake Titicaca boasts tremendous ecological significance, providing a sanctuary for various wildlife, including rare bird species. To preserve this precious natural and cultural resource, it is crucial to uphold sustainable tourism practices. At TooLacks, we are committed to promoting sustainable tourism and raising awareness of the importance of protecting our planet’s heritage.
We hope this article has inspired you to consider embarking on the adventure of a lifetime at Lake Titicaca and its islands. Remember to approach this unique destination with respect and appreciation for the local communities and the environment.
To learn more about Lake Titicaca and sustainable tourism, please visit UNESCO’s website or read National Geographic’s article.
So, pack your bags, and get ready for an unforgettable journey!